在Unity中,Button是我们最常用的组件之一了,它使用起来非常简单,例如监听一个Button点击事件
1 2 3 GetComponent<Button>().onClick.AddListener(() => { ... });
这样使用没有任何问题,但有时候我们会有疑问,为什么点击按钮onClick事件就会被触发呢?如何从回调函数中获取按钮的参数?让我们从源码中寻找答案。
查看源码前的配置 为了能够方便的查阅源码以及进行代码调试,需要重新导入UGUI包。新建Unity项目,找到Project/Packages/Unity UI,右键 Show in Explorer,将其复制到任意一个新的文件夹中(记住保存的位置,待会需要引用)。
接下来打开Window/Package Manager
找到Unity UI,将其Remove
然后点击“+”号,选择Add package form disk...,找到之前保存的UI包,进入目录后选中package.json,点击打开。
大功告成,现在我们可以查看/修改UGUI的源码了。
探究UGUI源码 通过F12打开Button代码,容易发现它继承Selectable类,同时还继承了IPointerClickHandler、ISubmitHandler接口,这两个接口分别会在鼠标点击、点击提交按钮时调用它们的回调函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class Button : Selectable, IPointerClickHandler, ISubmitHandler { [Serializable] //定义一个点击事件 public class ButtonClickedEvent : UnityEvent {} // 实例化一个ButtonClickedEvent的事件 [FormerlySerializedAs("onClick")] [SerializeField] private ButtonClickedEvent m_OnClick = new ButtonClickedEvent(); protected Button() {} //常用的onClick.AddListener()就是监听这个事件 public ButtonClickedEvent onClick { get { return m_OnClick; } set { m_OnClick = value; } } //如果按钮处于活跃状态并且可交互(Interactable设置为true),则触发事件 private void Press() { if (!IsActive() || !IsInteractable()) return; UISystemProfilerApi.AddMarker("Button.onClick", this); m_OnClick.Invoke(); } //鼠标点击时调用该函数,继承自 IPointerClickHandler 接口 public virtual void OnPointerClick(PointerEventData eventData) { if (eventData.button != PointerEventData.InputButton.Left) return; Press(); } //按下“提交”键后触发(需要先选中该游戏物体),继承自 ISubmitHandler //"提交"键可以在 Edit->Project Settings->Input->Submit 中自定义 public virtual void OnSubmit(BaseEventData eventData){...} private IEnumerator OnFinishSubmit(){...} }
IPointerClickHandler接口仅包含一个OnPointerClick()方法,当鼠标点击时会调用该接口的方法。而Button能触发点击事件是因为继承自IPointerClickHandler接口,并且重写了OnPointerClick方法。
那IPointerClickHandler接口的方法又是被谁调用的呢?查找引用,发现是ExecuteEvents类的Execute方法(该类相当于事件执行器,提供了许多通用的事件处理方法),并且Execute方法赋值给s_PointerClickHandler字段。
1 2 3 4 5 private static readonly EventFunction<IPointerClickHandler> s_PointerClickHandler = Execute;private static void Execute (IPointerClickHandler handler, BaseEventData eventData ){ handler.OnPointerClick(ValidateEventData<PointerEventData>(eventData)); }
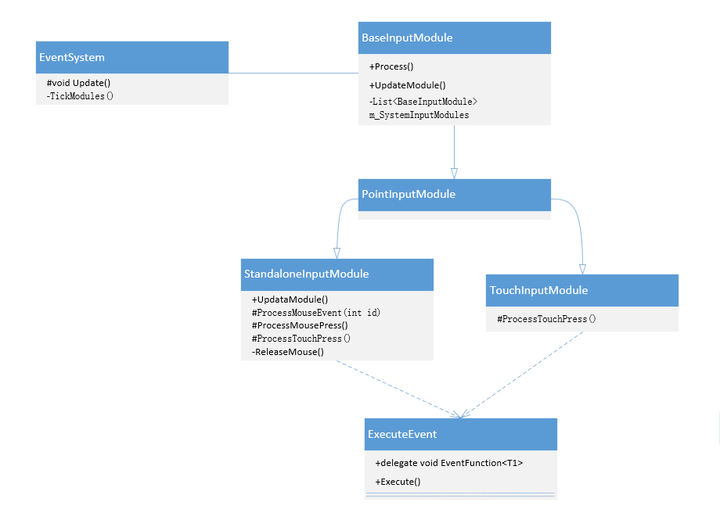
为了能看的更清楚,总结一下调用关系,即Button继承自Selectable、IPointercliClickHandler、ISubmitHandler,而IPointercliClickHandler、ISubmitHandler继承自IEventSystemHandler,ExecuteEvent会在鼠标松开时通过Execute函数调用IPointercliClickHandler、ISubmitHandler接口的方法,从而触发Button的onClick事件 ,如下图所示
继续往上找,ExecuteEvents类中还定义了一个EventFunction<T1>的泛型委托以及该委托类型的属性,这个返回s_PointerClickHandler,要查找谁触发的点击事件,只需要找到谁调用了pointerClickHandler即可
1 2 3 4 5 public delegate void EventFunction <T1 >(T1 handler, BaseEventData eventData )public static EventFunction<IPointerClickHandler> pointerClickHandler{ get { return s_PointerClickHandler; } }
容易发现,StandaloneInputModule和TouchInputModule类对其有调用,这两个类继承自BaseInput,主要用以处理鼠标、键盘、控制器等设备的输入, EventSystem类会在Update中每帧检查可用的输入模块的状态是否发生变化,并调用TickModules()和当前输入模块(m_CurrentInputModule)的Process()函数StandaloneInputModule的部分代码,它继承自BaseInputModule
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 protected void ProcessMousePress (MouseButtonEventData data ){ ... if (data.ReleasedThisFrame()) { ReleaseMouse(pointerEvent, currentOverGo); } ... } private void ReleaseMouse (PointerEventData pointerEvent, GameObject currentOverGo ){ ... if (pointerEvent.pointerPress == pointerUpHandler && pointerEvent.eligibleForClick) { ExecuteEvents.Execute(pointerEvent.pointerPress, pointerEvent, ExecuteEvents.pointerClickHandler); } ... }
查看ExecuteEvents.Execute的实现
上面已经查看过Execute方法,为什么现在又出来一个?ExecuteEvents中有N多个重载函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public static bool Execute <T >(GameObject target, BaseEventData eventData, EventFunction<T> functor ) where T : IEventSystemHandler{ var internalHandlers = s_HandlerListPool.Get(); GetEventList<T>(target, internalHandlers); for (var i = 0 ; i < internalHandlers.Count; i++) { T arg; try { arg = (T)internalHandlers[i]; } catch (Exception e) { var temp = internalHandlers[i]; Debug.LogException(new Exception(string .Format("Type {0} expected {1} received." , typeof (T).Name, temp.GetType().Name), e)); continue ; } try { functor(arg, eventData); } catch (Exception e) { Debug.LogException(e); } } var handlerCount = internalHandlers.Count; s_HandlerListPool.Release(internalHandlers); return handlerCount > 0 ; }
也就是说,EventSystem会在Update()中调用当前可用BaseInputModule的Process()方法,该方法会处理鼠标的按下、抬起等事件,当鼠标抬起时调用ReleaseMouse()方法,并最终调用Execute()方法并触发IPointerClick事件。 如下图所示(为了简洁,类图并不完整)
ReleaseMouse()是否只有鼠标左键抬起才会触发?Button在实现OnPointerClick()函数时忽略了鼠标中键和右键,使得只有左键能触发Button的点击事件
但现在还存在一个问题,怎么知道上述代码中事件执行目标target的值呢?探究这个问题之前,我们需要先对UGUI源码有个总体的认识,因为它涉及的知识点比较多。
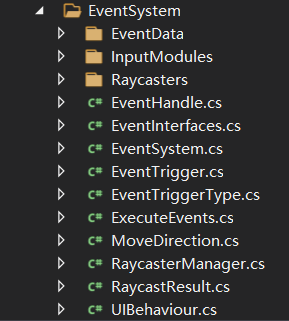
事件系统整体概述 我们先看EventSystem源码在文件夹中的分类
从图中就可以看出主要 包含三个子板块,分别是EvnetData、InputModules和Raycasters 。
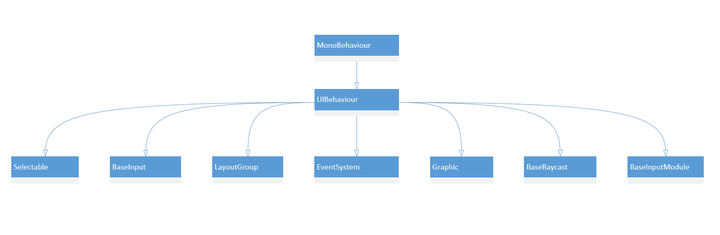
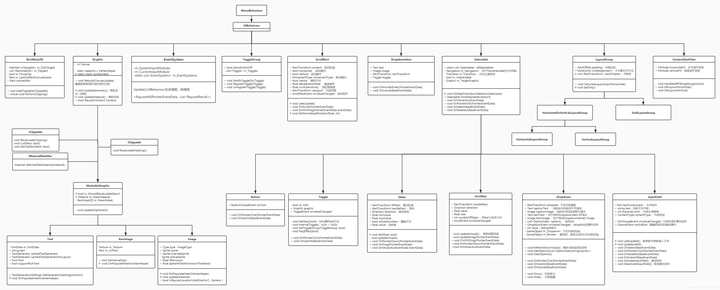
再看一个整体的类图,类图中包括了许多重要的类,如EventSystem、BaseRaycast、BaseInputModule等,它们都是继承自UIBehaviour,而UIBehaviour又是继承MonoBehaviour。(类图并不完整,只涉及部分类)
接下来对这些内容进行详细讲解。
EventSystem类事件系统主要是 基于输入(键盘、鼠标、触摸或自定义输入)向应用程序中的对象发送事件 ,当然这需要其他组件的配合。当你在GameObject中添加EventSystem时,你会发现它并没有太多的功能,这是因为 EventSystem本身被设计成事件系统不同模块之间通信的管理者和推动者
管理哪个游戏对象被认为是选中的 管理正在使用的输入模块 管理射线检测(如果需要) 根据需要更新所有输入模块
管理输入模块 下面看一下具体代码。首先是声明了BaseInputModule类型的List和变量,用来保存输入模块(Module)
1 2 3 4 private List<BaseInputModule> m_SystemInputModules = new List<BaseInputModule>();private BaseInputModule m_CurrentInputModule;
接下来,它会在Update中处理这些模块,调用TickModules方法,更新每一个模块,并且会在满足条件的情况下调用当前模块的Process方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 protected virtual void Update () { TickModules(); bool changedModule = false ; var systemInputModulesCount = m_SystemInputModules.Count; for (var i = 0 ; i < systemInputModulesCount; i++) { var module = m_SystemInputModules[i]; if (module.IsModuleSupported() && module.ShouldActivateModule()) { if (m_CurrentInputModule != module) { ChangeEventModule(module); changedModule = true ; } break ; } } if (m_CurrentInputModule == null ) { for (var i = 0 ; i < systemInputModulesCount; i++) { var module = m_SystemInputModules[i]; if (module.IsModuleSupported()) { ChangeEventModule(module); changedModule = true ; break ; } } } if (!changedModule && m_CurrentInputModule != null ) m_CurrentInputModule.Process(); } private void TickModules (){ var systemInputModulesCount = m_SystemInputModules.Count; for (var i = 0 ; i < systemInputModulesCount; i++) { if (m_SystemInputModules[i] != null ) m_SystemInputModules[i].UpdateModule(); } }
Process()方法主要是将各种输入事件(如点击、拖拽等事件)传递给EventSystem当前选中的GameObject(即m_CurrentSelected)
管理选中的游戏对象 当场景中的游戏物体(Button、Dropdown、InputField等)被选中时,会通知之前选中的对象执行被取消(OnDeselect)事件,通知当前选中的对象执行选中(OnSelect)事件,部分代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void SetSelectedGameObject (GameObject selected, BaseEventData pointer ){ ...... ExecuteEvents.Execute(m_CurrentSelected, pointer, ExecuteEvents.deselectHandler); m_CurrentSelected = selected; ExecuteEvents.Execute(m_CurrentSelected, pointer, ExecuteEvents.selectHandler); m_SelectionGuard = false ; }
管理射线检测 EventSystem中,还有一个非常重要的函数RaycastAll(),主要是获取目标。它被PointerInputModule类调用,大致来说是当鼠标设备可用或触摸板被使用时调用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public void RaycastAll (PointerEventData eventData, List<RaycastResult> raycastResults ) { raycastResults.Clear(); var modules = RaycasterManager.GetRaycasters(); var modulesCount = modules.Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < modulesCount; ++i) { var module = modules[i]; if (module == null || !module.IsActive()) continue ; module.Raycast(eventData, raycastResults); } raycastResults.Sort(s_RaycastComparer); }
它首先获取所有的BaseRaycast对象,然后调用它的Raycast方法,用以获取屏幕某个点下的所有目标(这个方法具体功能及实现的会在Raycast模块中进行讲解),最后对得到的结果进行排序,大部分情况都是根据深度(Depth)进行排序,在一些情况下也会使用距离(Distance)、排序顺序(SortingOrder,如果是UI元素则是根据Canvas面板的Sort order值,3D物体默认是0)或者排序层级(Sorting Layer)等作为排序依据。
讲了这么一大堆,来张图总结一下。**EventSystem会在Update中调用输入模块的Process方法来处理输入消息,PointerInputModule会调用EventSystem中的RaycastAll方法进行射线检测,RaycastAll又会调用BastRaycaster的Raycast方法执行具体的射线检测操作,主要是获取被选中的目标信息。**
简单概括一下UML图的含义,比如实线+三角形表示继承,实线+箭头表示关联,虚线+箭头表示依赖,关联和依赖的区别主要是引用其他类作为成员变量代表的是关联关系,将其他类作为局部变量、方法参数,或者引用它的静态方法,就属于依赖关系。
输入模块是配置和定制事件系统主逻辑的地方。 自带的输入模块有两个,一个是为独立输入(StandaloneInputModule),另一个是为触摸输入(TouchInputModule)。 StandaloneInputModule是PC、Mac&Linux上的具体实现,而TouchInputModule是IOS、Android等移动平台上的具体实现,每个模块都按照给定配置接收和分派事件。 运行EventSystem后,它会查看附加了哪些输入模块,并将事件传递给特定的模块。 内置的输入模块旨在支持常见的游戏配置,如触摸输入、控制器输入、键盘输入和鼠标输入等。
它的主要任务有三个,分别是
在讲Button的时候我们提到鼠标的点击事件是在BaseInputModule中触发的,除此之外,EventInterface接口中的其他事件也都是由输入模块产生的,具体触发条件如下:
当鼠标或触摸进入、退出当前对象时执行pointerEnterHandler、pointerExitHandler。
在鼠标或者触摸按下、松开时执行pointerDownHandler、pointerUpHandler。
在鼠标或触摸松开并且与按下时是同一个响应物体时执行pointerClickHandler。
在鼠标或触摸位置发生偏移(偏移值大于一个很小的常量)时执行beginDragHandler。
在鼠标或者触摸按下且当前对象可以响应拖拽事件时执行initializePotentialDrag。
对象正在被拖拽且鼠标或触摸移动时执行dragHandler。
对象正在被拖拽且鼠标或触摸松开时执行endDragHandler。
鼠标或触摸松开且对象未响应pointerClickHandler情况下,如果对象正在被拖拽,执行dropHandler。
当鼠标滚动差值大于零执行scrollHandler。
当输入模块切换到StandaloneInputModule时执行updateSelectedHandler。(不需要Input类)
当鼠标移动导致被选中的对象改变时,执行selectHandler和deselectHandler。
导航事件可用情况下,按下上下左右键,执行moveHandler,按下确认键执行submitHandler,按下取消键执行cancelHandler。
更加底层的调用还是UnityEngine.Input类,但可惜的是这部分Unity并没有开源。
每次事件系统中只能有一个输入模块处于活跃状态,并且必须与EventSystem组件处于相同的游戏对象上。
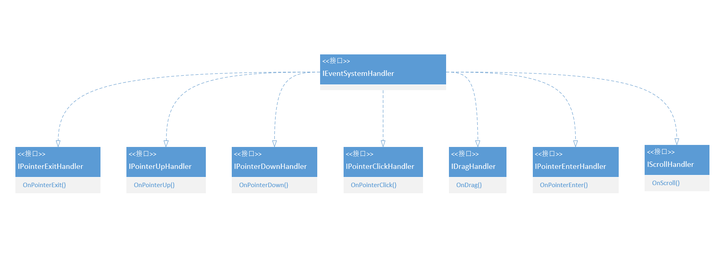
执行事件 既然InputModule主要就是处理设备输入,发送事件到场景对象,那这些事件是怎么执行的呢?在讲Button的时候,我们提到过ExecuteEvent类,其实事件的执行都是通过这个类进行的,不过也需要EventInterface接口配合。这个类中定义了许多接口,比如鼠标按下、点击、拖拽等,下图展示了部分接口的继承关系。
ExecuteEvent类中提供了一个方法让外部统一调用以执行事件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public static bool Execute <T >(GameObject target, BaseEventData eventData, EventFunction<T> functor ) where T : IEventSystemHandler{ var internalHandlers = s_HandlerListPool.Get(); GetEventList<T>(target, internalHandlers); var internalHandlersCount = internalHandlers.Count; for (var i = 0 ; i < internalHandlersCount; i++) { T arg; try { arg = (T)internalHandlers[i]; } catch (Exception e) { var temp = internalHandlers[i]; Debug.LogException(new Exception(string .Format("Type {0} expected {1} received." , typeof (T).Name, temp.GetType().Name), e)); continue ; } try { functor(arg, eventData); } catch (Exception e) { Debug.LogException(e); } } var handlerCount = internalHandlers.Count; s_HandlerListPool.Release(internalHandlers); return handlerCount > 0 ; }
这个方法之前有讲过,主要就是查找target对象上的T类型的组件列表,并遍历执行。
除此之外,还有一个GetEventHandler方法,它主要是通过冒泡的方式查找到能够处理指定事件的对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public static GameObject GetEventHandler <T >(GameObject root ) where T : IEventSystemHandler{ if (root == null ) return null ; Transform t = root.transform; while (t != null ) { if (CanHandleEvent<T>(t.gameObject)) return t.gameObject; t = t.parent; } return null ; } public static bool CanHandleEvent <T >(GameObject go ) where T : IEventSystemHandler { var internalHandlers = s_HandlerListPool.Get(); GetEventList<T>(go, internalHandlers); var handlerCount = internalHandlers.Count; s_HandlerListPool.Release(internalHandlers); return handlerCount != 0 ; }
比如我们在场景中创建一个Button,那这个Button还包含了Text组件,当鼠标点击的时候会调用GetEventHandler函数,该函数的root参数其实是Text,但是会通过冒泡的方式查找到它的父物体Button,然后调用Button的点击事件。
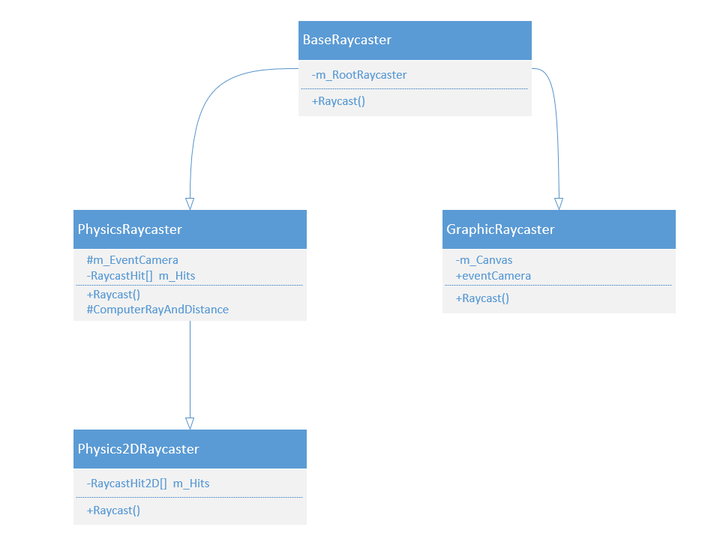
Raycasters事件系统需要一个方法来检测当前输入事件需要发送到哪里,这是由Raycasters提供的。 给定一个屏幕空间位置,它们将收集所有潜在目标,找出它们是否在给定位置下,然后返回离屏幕最近的对象。 系统提供了以下几种类型的Raycaster:
Graphic Raycaster: 检测UI元素Physics 2D Raycaster: 用于2D物理元素Physics Raycaster: 用于3D物理元素
BaseRaycaster是其他Raycaster的基类,这是是一个抽象类。在它OnEnable里将自己注册到RaycasterManager,并在OnDisable的时候从后者移除。
RaycasterManager是一个静态类,维护了一个BaseRaycaster类型的List,功能比较简单,包含获取(Get)、添加(Add)、移除(Remove)方法。
BaseRaycaster中最重要的就是Raycast方法了,它的子类都对该方法进行了重写。
Physics Raycaster它主要用于检测3D物理元素,并且保存被射线检测到物体的数据,下面是部分代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public override void Raycast (PointerEventData eventData, List<RaycastResult> resultAppendList ){ if (!ComputeRayAndDistance(eventData, ref ray, ref displayIndex, ref distanceToClipPlane)) return ; if (m_MaxRayIntersections == 0 ) { m_Hits = ReflectionMethodsCache.Singleton.raycast3DAll(ray, distanceToClipPlane, finalEventMask); hitCount = m_Hits.Length; } else { if (m_LastMaxRayIntersections != m_MaxRayIntersections) { m_Hits = new RaycastHit[m_MaxRayIntersections]; m_LastMaxRayIntersections = m_MaxRayIntersections; } hitCount = ReflectionMethodsCache.Singleton.getRaycastNonAlloc(ray, m_Hits, distanceToClipPlane, finalEventMask); } if (hitCount != 0 ) { if (hitCount > 1 ) System.Array.Sort(m_Hits, 0 , hitCount, RaycastHitComparer.instance); for (int b = 0 , bmax = hitCount; b < bmax; ++b) { var result = new RaycastResult { ... }; resultAppendList.Add(result); } } }
Physics2DRaycaster继承自PhysicsRaycaster,实现功能和方式基本一致,只不过是用于检测2D物体,这里不具体讲解
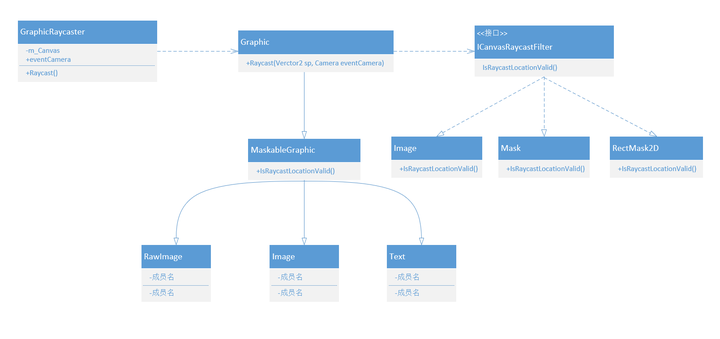
GraphicRaycastGraphicRaycast用于检测UI元素,它依赖于Canvas,我们在场景中添加Canvas默认都会包含一个GraphicRaycast组件。它先获取鼠标坐标,将其转换为Camera的视角坐标,然后分情况计算射线的距离(hitDistance),调用Graphic的Raycast方法来获取鼠标点下方的元素,最后将满足条件的结果添加到resultAppendList中。
一大波代码来袭,不感兴趣可以跳过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 public override void Raycast (PointerEventData eventData, List<RaycastResult> resultAppendList ){ if (canvas == null ) return ; var canvasGraphics = GraphicRegistry.GetRaycastableGraphicsForCanvas(canvas); if (canvasGraphics == null || canvasGraphics.Count == 0 ) return ; int displayIndex; var currentEventCamera = eventCamera; if (canvas.renderMode == RenderMode.ScreenSpaceOverlay || currentEventCamera == null ) displayIndex = canvas.targetDisplay; else displayIndex = currentEventCamera.targetDisplay; var eventPosition = Display.RelativeMouseAt(eventData.position); if (eventPosition != Vector3.zero) { int eventDisplayIndex = (int )eventPosition.z; if (eventDisplayIndex != displayIndex) return ; } else { eventPosition = eventData.position; } Vector2 pos; if (currentEventCamera == null ) { float w = Screen.width; float h = Screen.height; if (displayIndex > 0 && displayIndex < Display.displays.Length) { w = Display.displays[displayIndex].systemWidth; h = Display.displays[displayIndex].systemHeight; } pos = new Vector2(eventPosition.x / w, eventPosition.y / h); } else pos = currentEventCamera.ScreenToViewportPoint(eventPosition); if (pos.x < 0f || pos.x > 1f || pos.y < 0f || pos.y > 1f ) return ; float hitDistance = float .MaxValue; Ray ray = new Ray(); if (currentEventCamera != null ) ray = currentEventCamera.ScreenPointToRay(eventPosition); if (canvas.renderMode != RenderMode.ScreenSpaceOverlay && blockingObjects != BlockingObjects.None) { float distanceToClipPlane = 100.0f ; if (currentEventCamera != null ) { float projectionDirection = ray.direction.z; distanceToClipPlane = Mathf.Approximately(0.0f , projectionDirection) ? Mathf.Infinity : Mathf.Abs((currentEventCamera.farClipPlane - currentEventCamera.nearClipPlane) / projectionDirection); } #if PACKAGE_PHYSICS if (blockingObjects == BlockingObjects.ThreeD || blockingObjects == BlockingObjects.All) { if (ReflectionMethodsCache.Singleton.raycast3D != null ) { var hits = ReflectionMethodsCache.Singleton.raycast3DAll(ray, distanceToClipPlane, (int )m_BlockingMask); if (hits.Length > 0 ) hitDistance = hits[0 ].distance; } } #endif #if PACKAGE_PHYSICS2D if (blockingObjects == BlockingObjects.TwoD || blockingObjects == BlockingObjects.All) { if (ReflectionMethodsCache.Singleton.raycast2D != null ) { var hits = ReflectionMethodsCache.Singleton.getRayIntersectionAll(ray, distanceToClipPlane, (int )m_BlockingMask); if (hits.Length > 0 ) hitDistance = hits[0 ].distance; } } #endif } m_RaycastResults.Clear(); Raycast(canvas, currentEventCamera, eventPosition, canvasGraphics, m_RaycastResults); int totalCount = m_RaycastResults.Count; for (var index = 0 ; index < totalCount; index++) { var go = m_RaycastResults[index].gameObject; bool appendGraphic = true ; if (ignoreReversedGraphics) { if (currentEventCamera == null ) { var dir = go.transform.rotation * Vector3.forward; appendGraphic = Vector3.Dot(Vector3.forward, dir) > 0 ; } else { var cameraForward = currentEventCamera.transform.rotation * Vector3.forward * currentEventCamera.nearClipPlane; appendGraphic = Vector3.Dot(go.transform.position - currentEventCamera.transform.position - cameraForward, go.transform.forward) >= 0 ; } } if (appendGraphic) { float distance = 0 ; Transform trans = go.transform; Vector3 transForward = trans.forward; if (currentEventCamera == null || canvas.renderMode == RenderMode.ScreenSpaceOverlay) distance = 0 ; else { distance = (Vector3.Dot(transForward, trans.position - ray.origin) / Vector3.Dot(transForward, ray.direction)); if (distance < 0 ) continue ; } if (distance >= hitDistance) continue ; var castResult = new RaycastResult { ...... }; resultAppendList.Add(castResult); } }
上述代码中调用了Raycast函数重载,作用是向屏幕投射射线并收集屏幕下方所有挂载了Graphic脚本的游戏对象,该函数内容为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 private static void Raycast (Canvas canvas, Camera eventCamera, Vector2 pointerPosition, IList<Graphic> foundGraphics, List<Graphic> results ){ int totalCount = foundGraphics.Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < totalCount; ++i) { Graphic graphic = foundGraphics[i]; if (!graphic.raycastTarget || graphic.canvasRenderer.cull || graphic.depth == -1 ) continue ; if (!RectTransformUtility.RectangleContainsScreenPoint(graphic.rectTransform, pointerPosition, eventCamera, graphic.raycastPadding)) continue ; if (eventCamera != null && eventCamera.WorldToScreenPoint(graphic.rectTransform.position).z > eventCamera.farClipPlane) continue ; if (graphic.Raycast(pointerPosition, eventCamera)) { s_SortedGraphics.Add(graphic); } } s_SortedGraphics.Sort((g1, g2) => g2.depth.CompareTo(g1.depth)); totalCount = s_SortedGraphics.Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < totalCount; ++i) results.Add(s_SortedGraphics[i]); s_SortedGraphics.Clear(); }
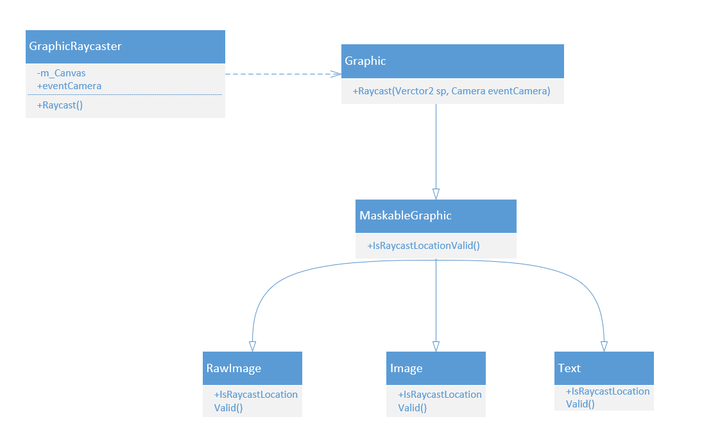
函数中又调用了Graphic类的Raycast函数,它主要是做两件事,一件是使用RectTransform的值过滤元素,另一件是使用Raycast函数确定射线击中的元素。 RawImage、Image和Text都间接继承自Graphic。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public virtual bool Raycast (Vector2 sp, Camera eventCamera ){ if (!isActiveAndEnabled) return false ; var t = transform; var components = ListPool<Component>.Get(); bool ignoreParentGroups = false ; bool continueTraversal = true ; while (t != null ) { t.GetComponents(components); for (var i = 0 ; i < components.Count; i++) { Debug.Log(components[i].name); var canvas = components[i] as Canvas; if (canvas != null && canvas.overrideSorting) continueTraversal = false ; var filter = components[i] as ICanvasRaycastFilter; if (filter == null ) continue ; var raycastValid = true ; var group = components[i] as CanvasGroup; if (group != null ) { if (ignoreParentGroups == false && group .ignoreParentGroups) { ignoreParentGroups = true ; raycastValid = filter.IsRaycastLocationValid(sp, eventCamera); } else if (!ignoreParentGroups) raycastValid = filter.IsRaycastLocationValid(sp, eventCamera); } else { raycastValid = filter.IsRaycastLocationValid(sp, eventCamera); } if (!raycastValid) { ListPool<Component>.Release(components); return false ; } } t = continueTraversal ? t.parent : null ; } ListPool<Component>.Release(components); return true ; }
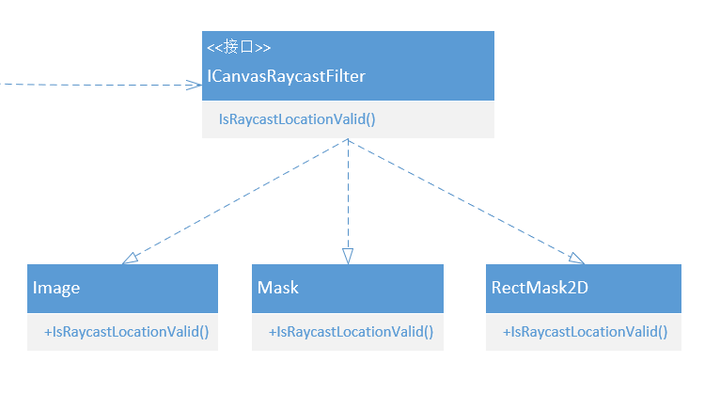
这里也使用了ICanvasRaycastFilter接口中的IsRaycastLocationValid函数,主要还是判断点的位置是否有效,不过这里使用了Alpha测试。Image、Mask以及RectMask2D都继承了该接口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public virtual bool IsRaycastLocationValid (Vector2 screenPoint, Camera eventCamera ){ if (alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold <= 0 ) return true ; if (alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold > 1 ) return false ; if (activeSprite == null ) return true ; Vector2 local; if (!RectTransformUtility.ScreenPointToLocalPointInRectangle(rectTransform, screenPoint, eventCamera, out local)) return false ; Rect rect = GetPixelAdjustedRect(); local.x += rectTransform.pivot.x * rect.width; local.y += rectTransform.pivot.y * rect.height; local = MapCoordinate(local, rect); Rect spriteRect = activeSprite.textureRect; float x = (spriteRect.x + local.x) / activeSprite.texture.width; float y = (spriteRect.y + local.y) / activeSprite.texture.height; try { return activeSprite.texture.GetPixelBilinear(x, y).a >= alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold; } catch (UnityException e) { Debug.LogError("Using alphaHitTestMinimumThreshold greater than 0 on Image whose sprite texture cannot be read. " + e.Message + " Also make sure to disable sprite packing for this sprite." , this ); return true ; } }
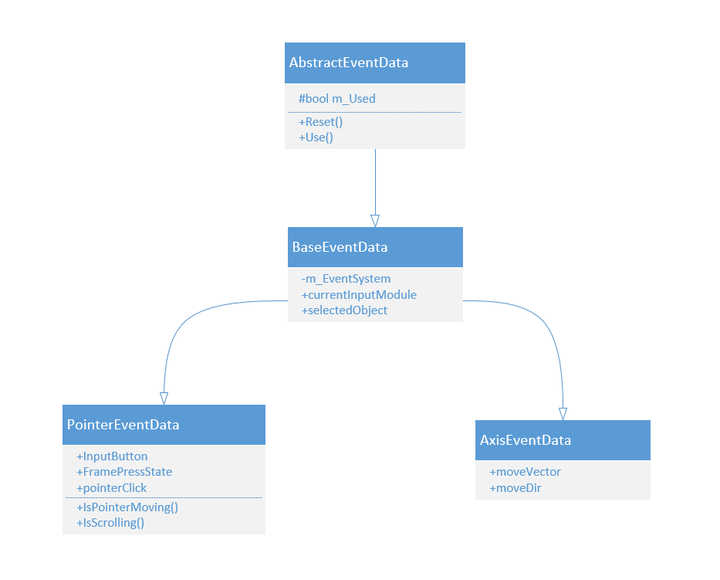
EventDataEventData用以存储事件信息,涉及到的东西不多,不展开讲解,层级关系如下图所示
在执行Button点击事件时,有些情况下我们需要获取触发事件的Button对象信息,这时可以自己实现一个Button点击事件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public class UIEventListener : MonoBehaviour , IPointerClickHandler , IPointerDownHandler , IPointerUpHandler { public delegate void PointerEventHandler (PointerEventData eventData ) public event PointerEventHandler PointerClick; public event PointerEventHandler PointerDown; public event PointerEventHandler PointerUp; public static UIEventListener GetEventListener (Transform transform ) { UIEventListener uIEventListener = transform.GetComponent<UIEventListener>(); if (uIEventListener == null ) uIEventListener = transform.gameObject.AddComponent<UIEventListener>(); return uIEventListener; } public void OnPointerClick (PointerEventData eventData ) { if (PointerClick != null ) PointerClick(eventData); } public void OnPointerDown (PointerEventData eventData ) { PointerDown?.Invoke(eventData); } public void OnPointerUp (PointerEventData eventData ) { PointerUp?.Invoke(eventData); } }
使用的时候,我们只需要将它挂载到Button组件上,然后在PointerClick事件中添加自己的处理函数。
总结 Button点击事件怎么触发的呢?首先是EventSystem在Update中调用当前输入模块的Process方法处理所有的鼠标事件,并且输入模块会调用RaycastAll来得到目标信息,通过冒泡的方式找到事件实际接收者并执行点击事件(这只是总体流程,中间省略很多具体步骤)。
最后来一张层级关系图